Antibacterial and deodorizing fabric
Release time: 2025-06-24
Antibacterial and deodorizing fabric
Which fabrics have antibacterial and deodorizing properties
Common antibacterial fabrics can be divided into natural fibers and chemical fibers. Let's talk about which fiber fabrics each have antibacterial properties
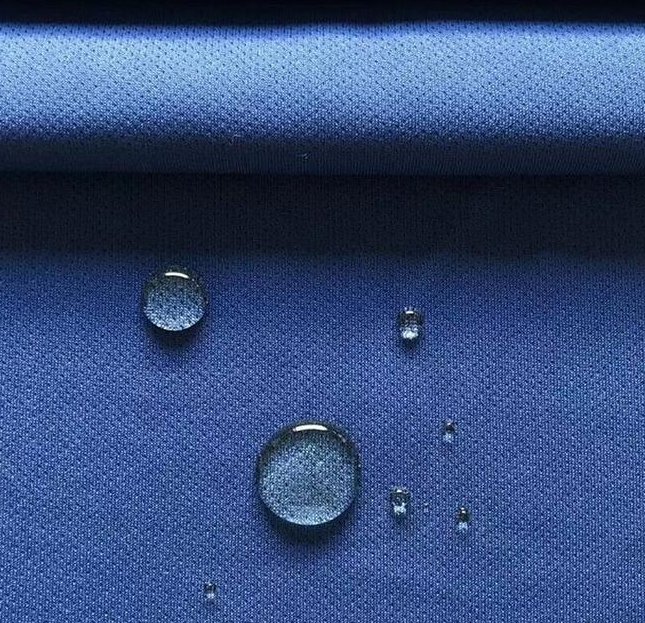

Bamboo fiber

Bamboo fiber contains the natural antibacterial substance "Zhukun", which can inhibit the growth of bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The fiber structure is porous and has strong moisture absorption, which can reduce the odor caused by sweat retention
Hemp fiber (flax/ramie)
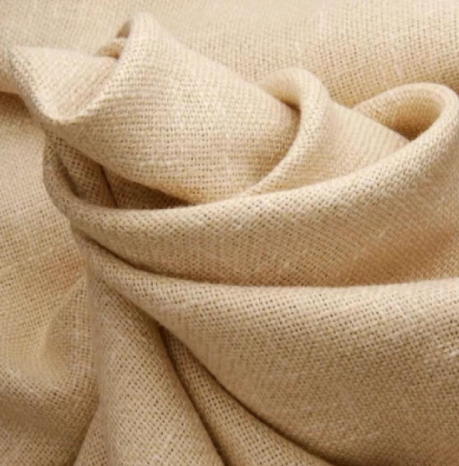

The surface of hemp fiber has a natural wax layer, with a loose fiber structure and excellent breathability and moisture wicking properties, which can reduce skin surface humidity and disrupt the environment for bacterial growth; And the "pectin" and "lignin" contained in hemp fiber have certain antibacterial effects
Natural fiber fabric
Wool (natural antibacterial wool)
The scale structure on the surface of high-quality wool fibers and natural oils (lanolin) can inhibit the growth of some bacteria, and wool can absorb 30% of its own weight of water without producing a damp feeling, reducing the source of odors

Chemical fiber
Or modified fibers
Polyester fiber (polyester)/nylon (nylon)+antibacterial finishing

By adding antibacterial agents (such as silver ions, zinc ions, organic antibacterial agents) through post-processing processes (such as immersion rolling, coating), antibacterial agents can damage bacterial cell membranes or inhibit their enzyme activity, achieving antibacterial effects
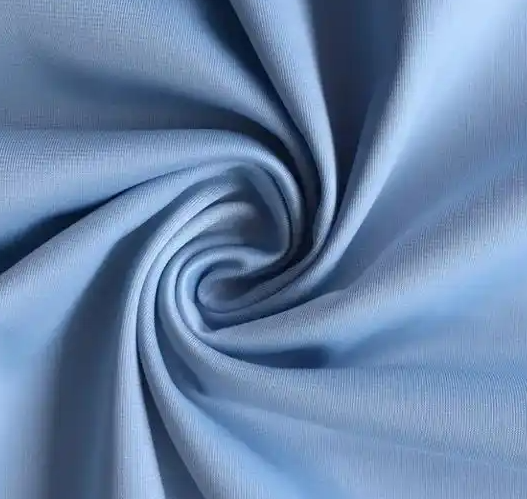

By adding antibacterial agents (such as silver ions, zinc ions, organic antibacterial agents) through post-processing processes (such as immersion rolling, coating), antibacterial agents can damage bacterial cell membranes or inhibit their enzyme activity, achieving antibacterial effects
Modal/viscose fiber+antibacterial treatment
After modification, natural wood pulp fibers are combined with antibacterial agents (such as chitosan and quaternary ammonium salts) to maintain softness and moisture absorption while enhancing antibacterial properties
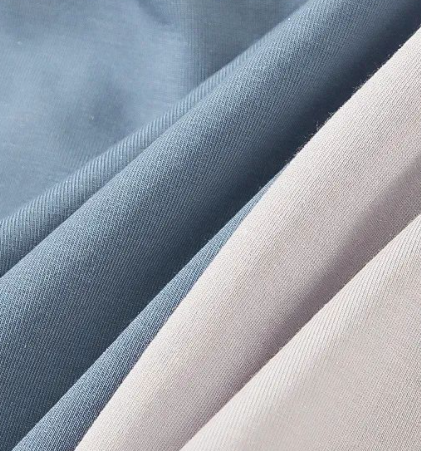

Acrylic fiber (acrylic)+antibacterial modification
Introducing antibacterial groups into the fiber molecular structure through copolymerization reaction, or surface grafting antibacterial agents to inhibit the growth of fungi (such as mold) and bacteria

 Suzhou-Jiangsu-China
Suzhou-Jiangsu-China +0512-63373373
+0512-63373373 info@shangyutex.com
info@shangyutex.com
