Mid Autumn Festival and National Day | One Reward for Fabric Quality
Release time: 2025-10-01
Mid Autumn Festival and National Day
No matter how far apart we are, admiring the quality of the fabric, the moonlight pouring down, longing overflowing, or being close to each other, it is another year of Mid Autumn Festival, which is a footnote to reunion
Full Moon, Deep Affection
Lighting up fabric moment
How is the fabric developed
Fabric development is a systematic process that integrates market demand, material science, process technology, and sustainable concepts, requiring full chain control from requirement definition to mass production implementation. Each link needs to be precisely connected to ensure that the final product meets design, functional, and cost goals

Early stage
Clearly define development goals and requirements
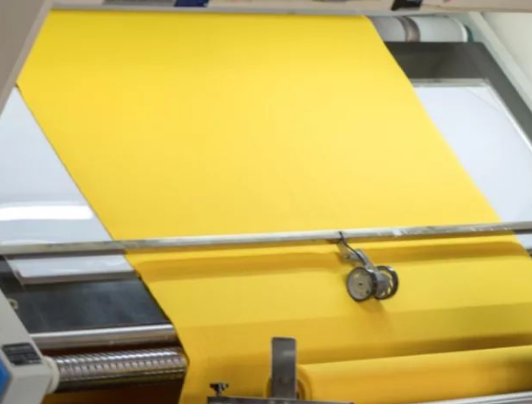

Mid term
Core development process

This stage is the core of transforming the fabric from a "concept" to a "physical sample", which involves five steps: fiber selection, yarn preparation, weaving/knitting, dyeing and finishing, and functional finishing. Each step affects the final performance of the fabric.
The first step
Fiber selection
Fiber is the foundation of fabrics, and its type directly determines the texture, functionality, and characteristics of the fabric. Natural fibers, chemical fibers, or mixed fibers should be selected according to the development goals: natural fibers such as cotton, wool, silk, and linen;
Chemical fibers: such as polyester, nylon, spandex, recycled fibers, Tencel, meet sustainable needs;
Blended fiber: Combining the advantages of two types of fibers, such as "cotton+polyester", "wool+nylon", "linen+cotton".
Step 2
Yarn preparation
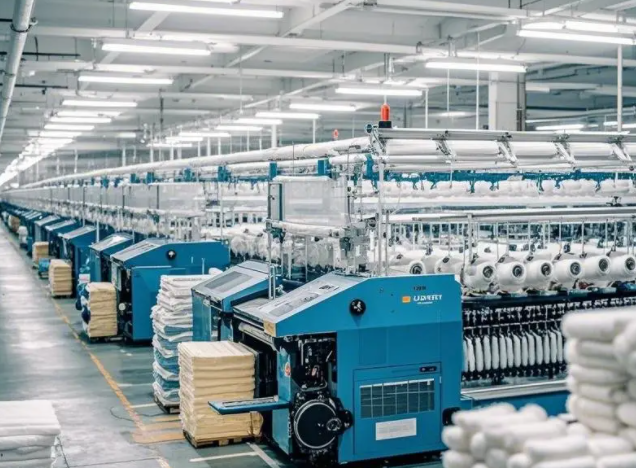

Fibers need to be processed into "yarn" before they can be used for weaving/knitting. The process of yarn determines its thickness, strength, and style: spinning process: ring spinning: yarn structure is tight and delicate, suitable for high-end fabrics; Airflow spinning: yarn fluffy, wear-resistant, low cost, suitable for denim and sweatshirt fabrics;
Vortex spinning: fast spinning speed, smooth yarn, good elasticity, suitable for sports fabrics; Yarn form: Single yarn: Twisted single strand fibers, suitable for lightweight fabrics; Strand: Twisting multiple strands of single yarn together for higher strength, suitable for wear-resistant fabrics; Special yarns: such as bamboo yarn, core spun yarn, and fancy yarn.
The third step
Weaving/Knitting

Process yarn into "fabric" through "weaving" or "knitting" techniques, which correspond to different fabric structures and textures
Step Four
Dyeing and Finishing Processing
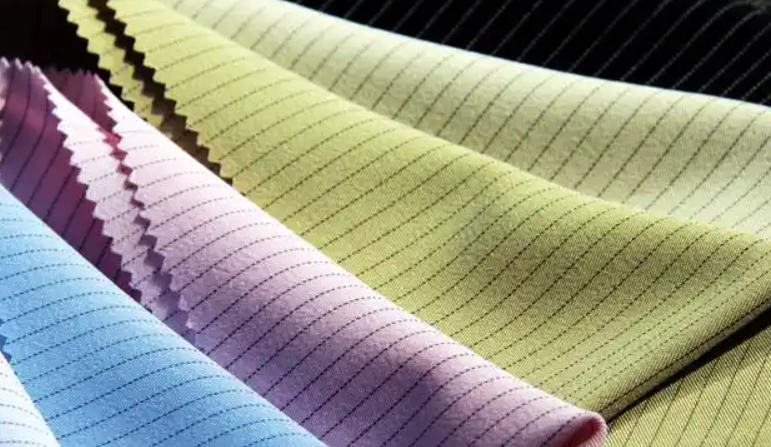

Step Five
Post functional organization
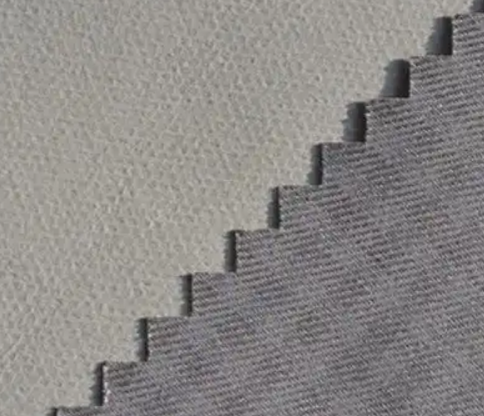

If the development goal includes functionality such as waterproofing and antibacterial, it is necessary to add functionality after dyeing and finishing before finishing
 Suzhou-Jiangsu-China
Suzhou-Jiangsu-China +0512-63373373
+0512-63373373 info@shangyutex.com
info@shangyutex.com
