Wear resistant fabric
Release time: 2024-12-17
Wear resistant fabric
The most durable fabrics are them
Related to the breaking strength and strength of warp and weft yarns
It is related to factors such as the material and blending ratio of the fiber raw materials used for yarn formation, the fineness of the fiber itself (count or special number) and the fineness of the yarn (count or special number), the uniformity of yarn formation, moisture regain or moisture content, whether it is a single yarn or a stranded thread, the twist (twist coefficient) of single yarn and stranded thread, and the storage life of the fiber or yarn. Elastic fibers, including their elongation rate, can cause significant differences



Related to the weaving method and weaving conditions of the fabric
Related to knitted and woven fabrics, organizational structure (such as plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, jacquard, etc.), and warp and weft yarn density.
The warp strength and weft strength are different, and the breaking strength is also different. Whether there is a fabric edge, whether it is a solid edge or a rough edge, whether it avoids defects and wrinkles, and the distance from the original fabric edge may vary (so sampling must be at least 15cm away from the fabric edge).
In addition, the strength of the sizing fabric and the desizing fabric, as well as the dyed and post processed fabrics, especially the impregnated and specially processed fabrics, will vary greatly. Weaving techniques, dyeing, sanding, and so on all have an impact. Coarse yarns exhibit better strength than fine yarns, twill yarns are better than plain weave, unpolished yarns are better than brushed yarns, and the less corrosive dyeing is, the better.
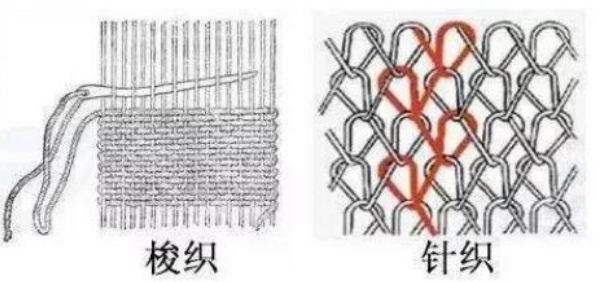
Related to yarn strength and warp and weft density
To improve the strength of yarn dyed fabrics, we need to focus on these two aspects. The tensile and tear strength of non ironing fabrics will also decrease after non ironing finishing, directly affecting the durability of the fabric. The tensile and tear strength, yarn strength and elongation, interlacing resistance, and morphological structure of fabrics before and after non ironing finishing have a significant impact on strength.
When fabrics woven from yarns with high strength and elongation are torn, the force triangle area is larger, and the number of yarns that are jointly subjected to force is higher, resulting in higher tearing strength. The organizational structure and warp and weft yarn density affect the interlacing points and slippage between yarns. With fewer interlacing points, yarns are prone to slippage, resulting in higher tearing strength of the fabric. After a period of wearing, clothing often experiences sudden tearing due to friction that causes the yarns in the fabric to become thinner.
When squatting, certain parts of the pants buttocks and clothing that are hooked by sharp objects are subjected to external forces, causing the yarns inside the fabric to break one by one under extreme load. During the use of textiles, if they are subjected to local concentrated loads for a long time, the strength may reach its limit and decrease, thereby affecting the tensile and tear strength of the fabric.

What fabric is good and resistant to friction
Nylon fabric
Nylon was developed by outstanding American scientist Carothers and a research team under his leadership, and is the world's first synthetic fiber.
Nylon fabric has the highest wear resistance among all types of fabrics, with a wear resistance 10 times higher than cotton and 20 times higher than wool. Adding some polyamide fibers to blended fabrics can greatly improve their wear resistance; When stretched to 3-6%, the elastic recovery rate can reach 100%; Can withstand tens of thousands of twists and turns without breaking. It is many times higher than other fiber fabrics in the same category, therefore, its durability is excellent. Clothing made of nylon is suitable for making hiking clothes, winter clothes, etc.
oxford
Oxford cloth, also known as Oxford spinning. Originating in the UK and named after the University of Oxford, Oxford cloth is a traditional combed cotton fabric that began around 1900. Using finer combed high count yarn as double warp, interwoven with thicker weft yarn in a weft weight flat weave.
Soft color, soft fabric body, good breathability, comfortable to wear, easy to wash and dry quickly, often used as shirts, sportswear, pajamas, etc. It has advantages such as good waterproofing and durability, and is also used to make bags and suitcases. There are many varieties of products with various styles, including plain colors, bleached colors, warp and weft colors, warp and weft colors, medium and light colored striped patterns, etc; It is also woven with polyester cotton yarn.


 Suzhou-Jiangsu-China
Suzhou-Jiangsu-China +0512-63373373
+0512-63373373 info@shangyutex.com
info@shangyutex.com
